Crispr Cas
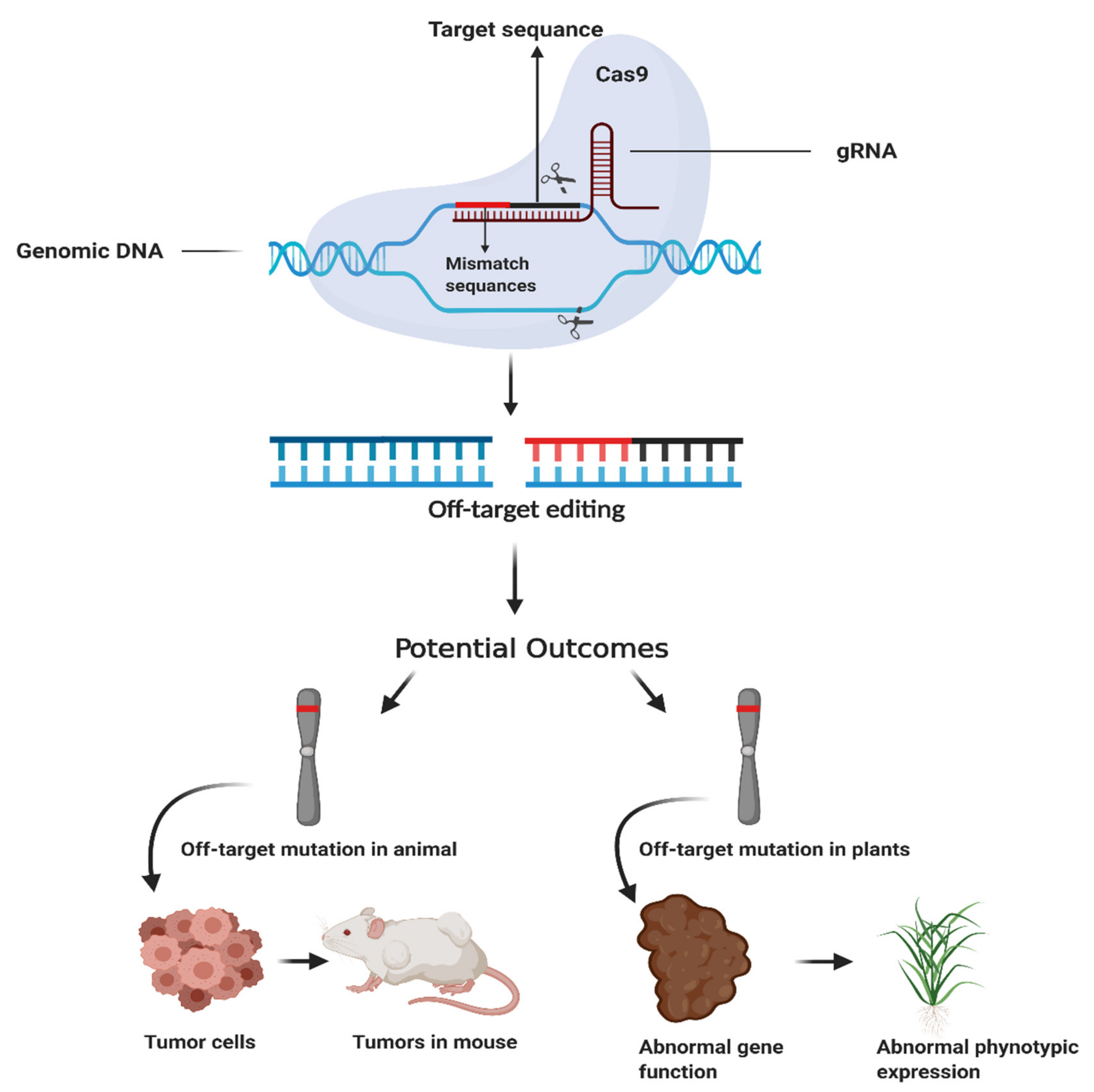
Among the currently known prokaryotic defense systems the crispr cas genomic loci show unprecedented complexity and diversity.
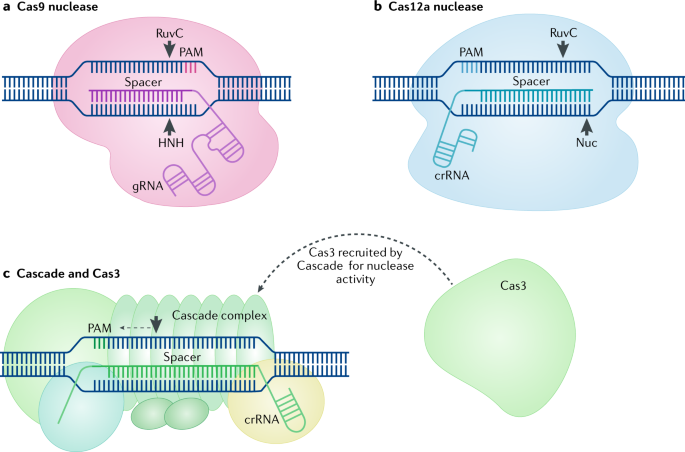
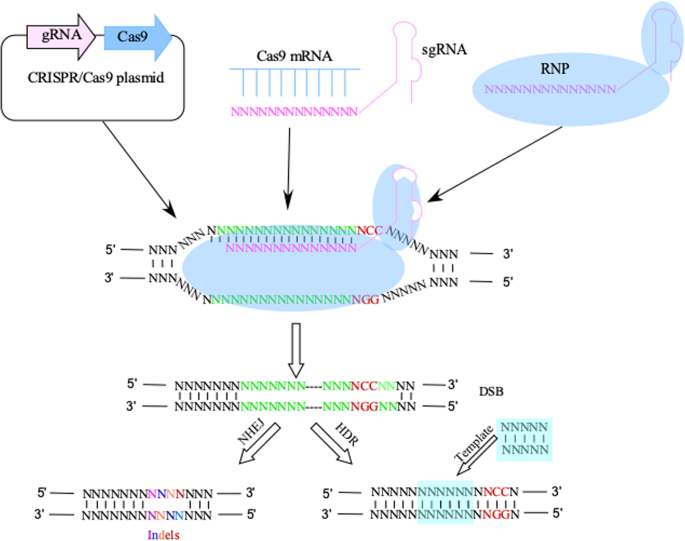
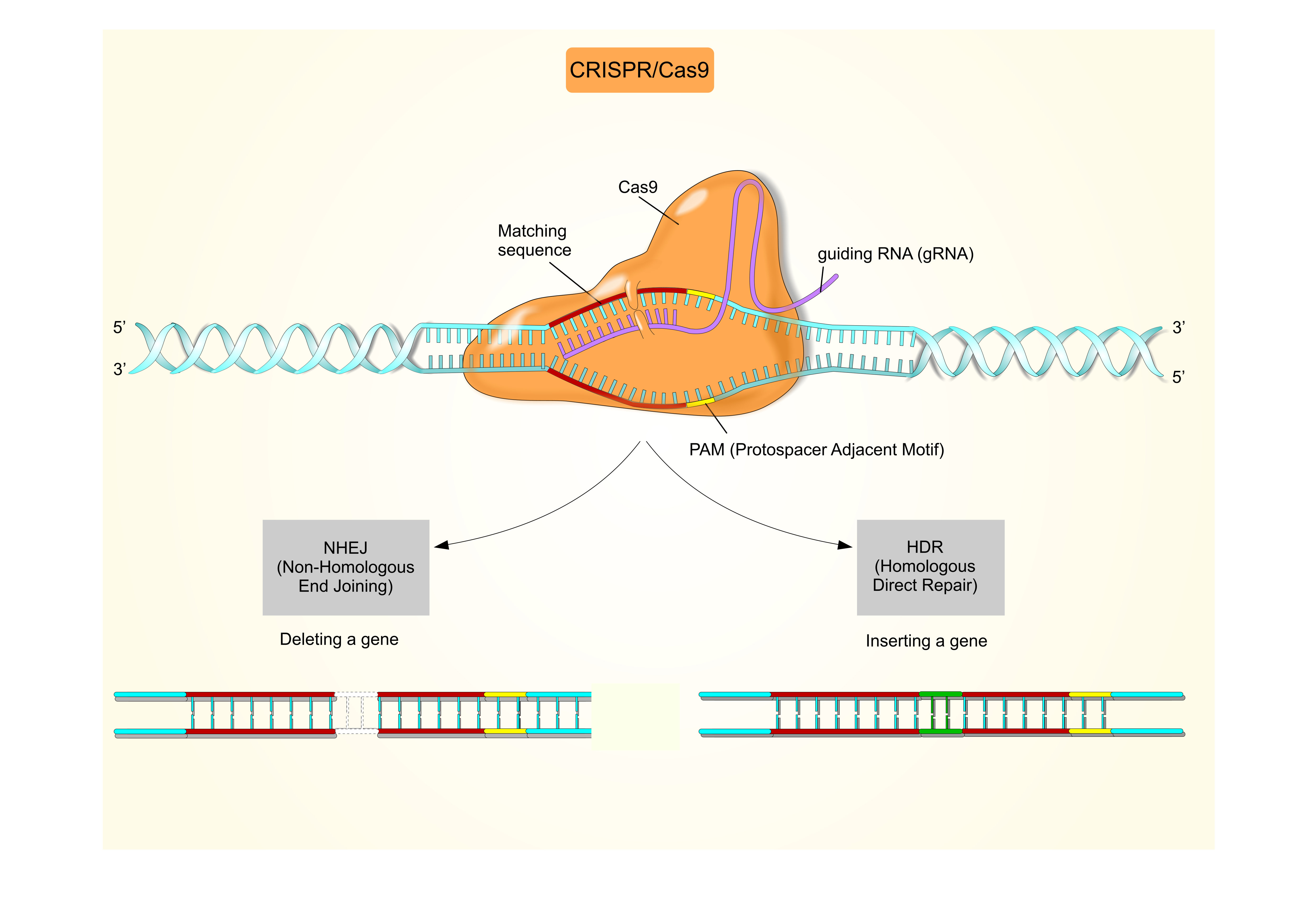
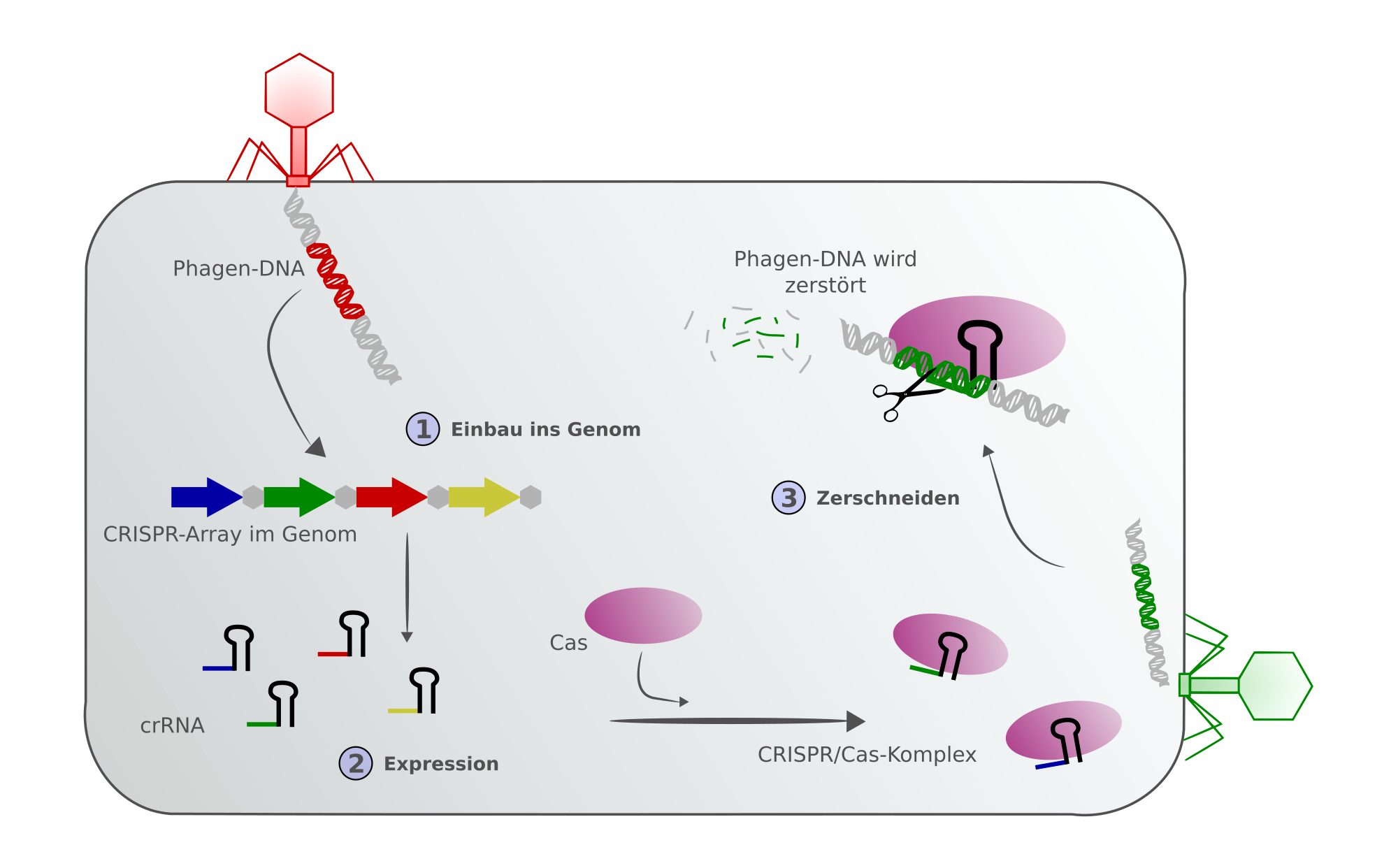
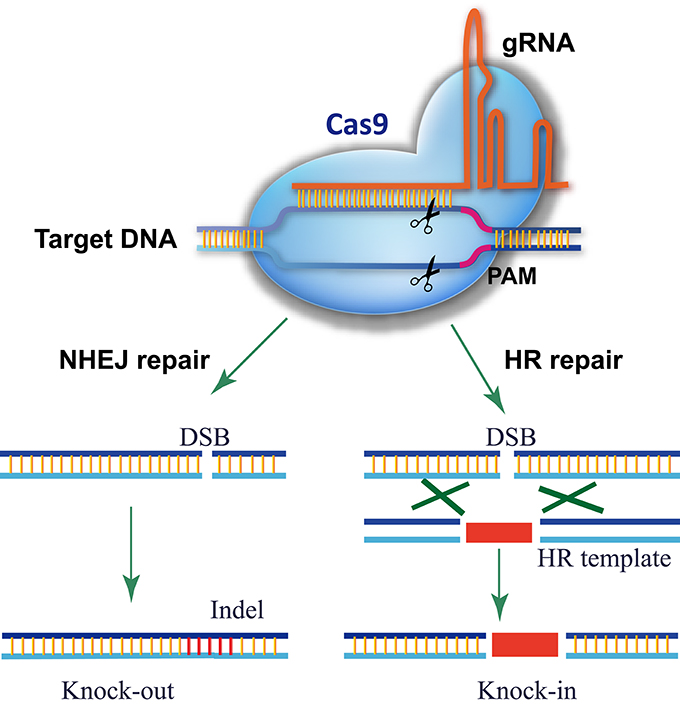
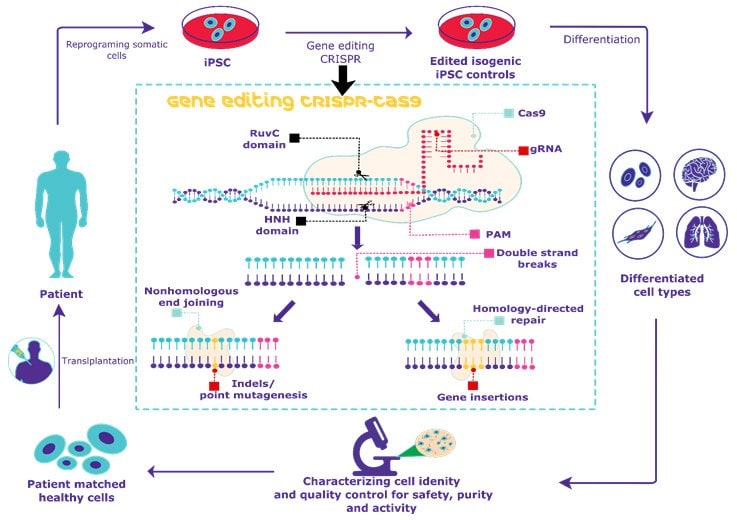
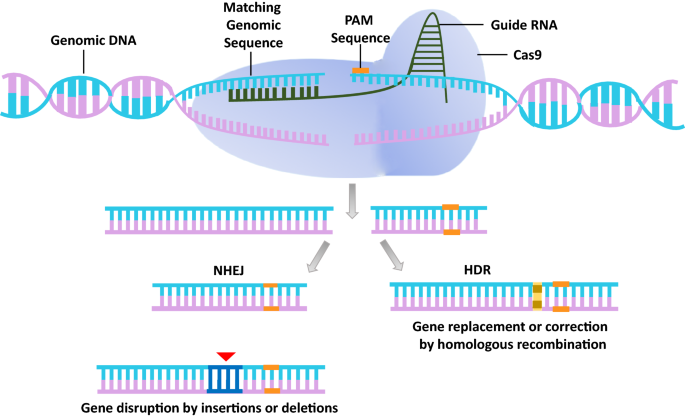
Crispr cas. The crispr cas system is a prokaryotic immune system that confers resistance to foreign genetic elements such as those present within plasmids and phages and provides a form of acquired immunity rna harboring the spacer sequence helps cas crispr associated proteins recognize and cut foreign pathogenic dna. Crispr cas9 is a unique technology that enables geneticists and medical researchers to edit parts of the genome. It is currently the simplest most versatile and precise method of genetic manipulation and is therefore causing a buzz in the science world. Crispr cas9 crispr gene editing is a genetic engineering technique in molecular biology by which the genomes of living organisms may be modified.
The bacteria capture snippets of dna from invading viruses and use them to create dna segments known as crispr arrays. It is based on a simplified version of the bacterial crispr cas9 antiviral defense system. By removing adding or altering sections of the dna. The crispr arrays allow the bacteria to remember the viruses or closely related ones.
The idt alt r crispr cas systems work as follows. The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats crispr cas crispr associated proteins is a prokaryotic adaptive immune system that is represented in most archaea and many bacteria. For the prokaryotic antiviral system see crispr. Crispr cas9 was adapted from a naturally occurring genome editing system in bacteria.